The Relationship Between OEE and P&L: How to Improve OEE
Many businesses overlook the relationship between Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and Profit & Loss (P&L). What these businesses need to realize is that improving OEE can have a major impact on the bottom line. So first, we’ll discuss the relationship between OEE and P&L and some strategies for improving OEE.
How to calculate Overall Equipment Effectiveness in manufacturing plants?
OEE is a term first used in the 1960s by Seiichi Nakajima as part of his Total Productive Maintenance program. It measures how well a manufacturing operation is utilized and is calculated by multiplying three factors: Availability, Performance, and Quality.
The first step in calculating OEE is to determine your plant’s Availability.
This is the percentage of time that your equipment is operational and available for use. To sum it up, divide the total amount of time your equipment is active by the total amount of time it could be functional. For example, if your equipment is operational for 8 hours out of 10, your Availability would be 80%.
Baca Juga: Pentingnya Perhitungan OEE untuk Mesin Pabrik
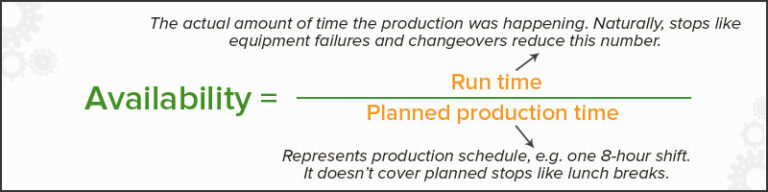
(Run Time = Planned Production Time – all planned and unplanned stops)
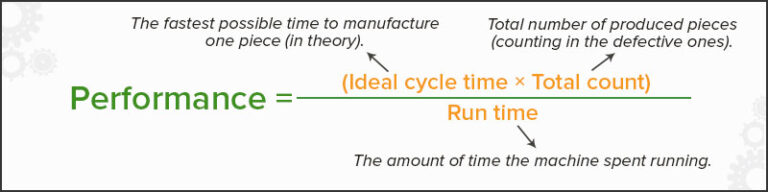
The second step is to calculate performance.
This considers slowdowns due to start-up or shut-down procedures and breaks for maintenance or repairs. To calculate performance, you need to know two things: your equipment’s Ideal Cycle Time (the minimum amount of time necessary to produce one good unit) and your Actual Cycle Time (the actual amount of time required to make one good team). Once you have those numbers, divide your Actual Cycle Time by your Ideal Cycle Time. For example, if it takes 5 minutes to produce one good unit, but it could take 4 minutes if everything went perfectly, then your performance would be 80%.
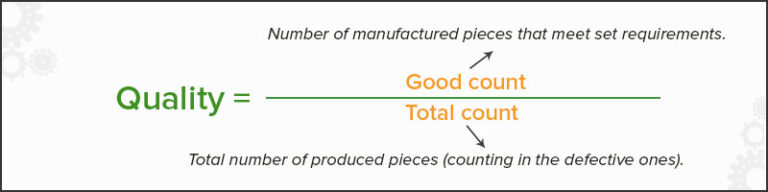
The last step in calculating OEE is Quality.
Quality accounts for scrapped units, units that fail inspection. To calculate the Quality, you need to know two things: the Total Units Produced during the shift and the number of Good Units Produced during the change. Good Units are units that meet all quality standards set forth by the customer or end user. To calculate the Quality, divide the number of Good Units by the Total Units Produced. For example, if you produce 1,000 units and 950 of them are good during a shift, your Quality would be 95%.
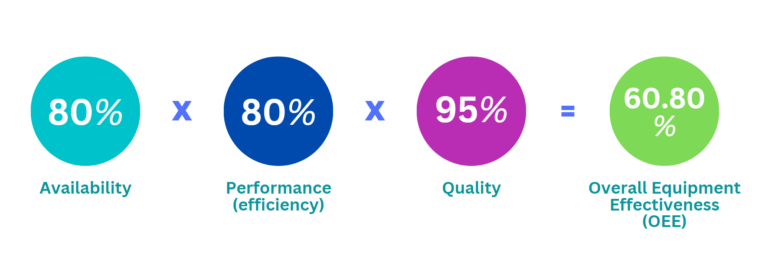
Now that we’ve gone over how to calculate the three individual components of OEE—Availability, Performance, and Quality—we can put them all together to get an overall picture of how effectively our manufacturing plant is running. To do this, multiply Availability x Performance x Quality. Using our earlier examples
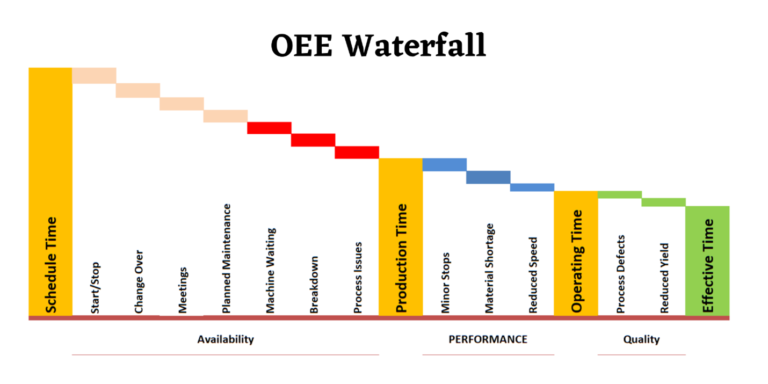
OEE Waterfall Chart: The chart below illustrates all potential root courses that contribute to the result of OEE in Availability, Performance and Quality.
How Does OEE Impact P&L?
OEE impacts P&L in two ways: through production losses and scrap costs. Production losses occur when machines are down or running at less than full capacity; this results in lost production time and opportunities. Scrap costs arise when machines produce defective parts; these parts must either be reworked or scrapped completely, which incurs additional charges. By reducing production losses and scrap costs, businesses can improve their P&L statement.

Now that we’ve discussed how OEE impacts P&L, let’s take a look at some strategies for improving OEE:
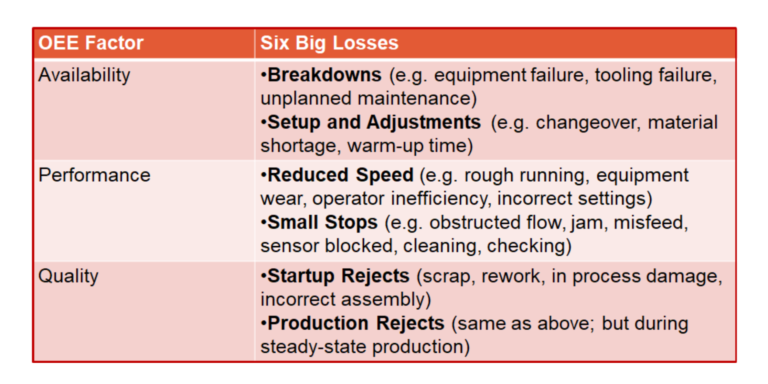
Expand to the Six Big Losses
The three OEE factors, Availability, Performance, and Quality, are associated with six extremely common losses in discrete manufacturing. As a result, the Six Big Losses are an outstanding framework for understanding and, most importantly, for taking action on losses exposed through your OEE initiative.
How can I improve my company’s OEE?
Many factors contribute to OEE, and each company is different, so it is important first to assess to see where there is room for improvement. Once you have identified areas for improvement, there are some general steps you can take to improve your company’s OEE:
 | Instead of how many products you can produce in a day, think about how you can make each product as efficiently as possible. Every minute counts when it comes to maximizing the utilization of your resources. |
 | Get buy-in from all levels of your organization by communicating why improvements in OEE are important. Set goals and reward employees who help meet those goals. |
 | There are proven best practices for maximizing the utilization of resources that can be adapted to fit your company’s specific needs. For example, one best practice is single-piece flow, a lean manufacturing technique that involves producing one product at a time instead of batching products together. This helps minimize WIP inventory and reduces dependencies between workers, which leads to increased throughput and decreased operational expenses. |
 | Many software solutions can help you track and improve your company’s OEE. For example, the Manufacturing execution system (MES) includes an OEE Module that gives users visibility into all aspects of their production process so they can identify bottlenecks and make data-driven decisions to improve the utilization of resources. |
 | Machines require periodic maintenance to run efficiently. This includes tasks such as cleaning, lubricating, and replacing worn-out parts. Regularly maintaining your machines can reduce downtime and keep them running at peak performance levels. |
 | Lean manufacturing techniques such as 5S (sort, set in order, shine/clean, standardize items/processes/operator actions), kanban (pull system), single-minute exchange of dies (SMED), value stream mapping (VSM), etc., can help streamline processes and improve OEE levels. |
 | In lean production, waste does not add value to the product or service. Instead, lean production is about efficiency and eliminating waste to create a more streamlined manufacturing process. There are seven main types of waste in lean production. They are overproduction, waiting, transportation, processing, inventory, motion, and defects. We will discuss each type of waste in detail and provide tips on avoiding them. |
 |
| Transportation occurs when products or materials are moved unnecessarily throughout the manufacturing process. This can happen if products are transferred between departments or raw materials are stored in multiple locations. Transportation can lead to wasted time and resources. To avoid transportation waste, you should streamline the manufacturing process so that products must only be transported once between departments. Raw materials should also be stored in a central location for easy access by all employees involved in the production process. |
 |
| Inventory occurs when there are excessive raw materials or finished products stored on site. This can happen if products are produced ahead of schedule or raw materials must be used promptly. Inventory can lead to storage problems and decreased cash flow. To avoid inventory waste, you should implement just-in-time methods to ensure that raw materials are only delivered when needed. You should also review your production schedule regularly to see if there are any areas where you can cut down on inventory levels. |
 |
| Motion occurs when employees travel excessive distances while performing their duties. This can happen if workers have to walk long distances to retrieve supplies or if they have to operate machinery that is not nearby. Motion can lead to wasted time and resources. To avoid motion waste, you should rearrange your workplace so that employees have everything they need within proximity. It would be best if you also considered investing in ergonomic equipment that reduces the amount of travel required by employees. |
 |
| Waiting occurs when there is a delay in the manufacturing process. This can be due to needing more raw materials, waiting for approval from another department, or waiting for equipment to become available. Waiting can lead to delays in the production process and decreased efficiency. To avoid waiting, you should implement just-in-time methods to ensure that raw materials are available when needed and that all manufacturing departments know their deadlines. In addition, it would be best to cross-trained employees so they can work on multiple tasks during downtime. |
 |
| Overproduction occurs when more of a product is created than is needed. This can happen for several reasons, such as making products ahead of schedule or producing too much of a product to meet customer demand. Overproduction can lead to increased costs and decreased efficiency. To avoid overproduction, you should only have what is needed when it is required. This can be accomplished by using just-in-time production methods and flexible manufacturing processes. |
 |
| Processing occurs when excessive time or resources are spent on producing a product. This can happen if there are too many steps in the manufacturing process or if workers need to be trained to properly use equipment. As a result, processing can lead to decreased efficiency and increased costs. To avoid processing waste, you should streamline the manufacturing process by eliminating unnecessary steps and ensuring that all workers are properly trained on how to use equipment efficiently. |
 |
| Defects occur when products do not meet quality standards and must be reworked or scrapped. This can happen if there needs to be better communication between departments or workers need proper training. Defects can lead to increased costs and decreased customer satisfaction. To avoid deficiencies, you should implement quality control measures at every stage of the manufacturing process. You should also ensure that all workers are properly trained on performing their job duties correctly. |
Conclusion:
Improving overall equipment effectiveness (OEE) can significantly impact profitability; however, many businesses overlook the relationship between OEE and profit & loss (P&L). We discussed how OEE impacted P&L through production losses and scrap costs and shared some strategies for improving OEE levels within your organization. Implementing these strategies can improve your bottom line while reducing production losses and scrap costs.
By regularly calculating OEE for our manufacturing plants, we can stay on top of our operation’s effectiveness and make changes as necessary to keep things running smoothly.

Industry Leader I Author I Speaks regularly at | IoT | Industry 4.0 | Smart Manufacturing | Digital Transformation | Energy | 30K Followers

